The 16 Intertype Relationships: Socionics Intertype Relations
What are Intertype Relations?
Socionics intertype relations offer a depth of insight through functional interaction between types. Intertype relations are based on psychological compatibility through shared process functions. It can help to explain why we feel comfortable easily with some people versus others or even why we feel an uncontrollable attraction to certain psychological types.
This article will give you a nice overview summary of intertype relations. However, please visit individual articles of each intertype relation to get a complete understanding of that particular relationship and intertype interaction.
How is Socionics different from MBTI?
Socionics differs from MBTI because Aushra Augusta incorporated Antoni Kepinski’s concept of information metabolism along with Carl Jung’s psychological types. Socionics goes even more in depth than MBTI, because of its ingenius combining of Kepinski’s information metabolism, Freud’s structural theory, and Jung’s psychological types.
The theories of Socionics developed primarily in Eastern European and former Soviet Union countries. Its founder Aushra Augusta is from Lithuania, while another prominent developer Viktor Gulenko is based out of Kyiv, Ukraine. Socionics naming system of Socionics types differs from MBTI, because it uses only 3 letters although each type correlates perfectly to one MBTI type.
This article is written with MBTI terms of naming the types instead of Socionic types. I am starting a series on my website that I will call “Model X” to publish Socionics ideas in MBTI terms to share this wealth of knowledge with more people. I dream that one that the insightful concepts from Socionics will reach all parts of the world just as MBTI has.
Okay, let’s get into these intertype relations so that you can learn about compatible types!
What are the types of intertype relations?
These classification terms assist in describing the effect of the relation.
Inner-quadra relations: shared between members of the same quadra (alpha, beta, gamma, delta), which indicates that all four conscious functions are shared but in a different order. Mutual respect and communication is often easy, if not effortless with types in the same quadra.
Outer-quadra relations: types are of different quadras, which means that at least half (if not all) of their functions differ from each other

Symmetric relations: affect both types equally in the same way
Asymmetric relations: affect the types asymmetrically, which means that one partner is often in admiration or in service of the other type (I find that the asymmetric relations revolve around teaching and learning in different proportions with each other.)
Inner-Quadra Symmetric Relationships
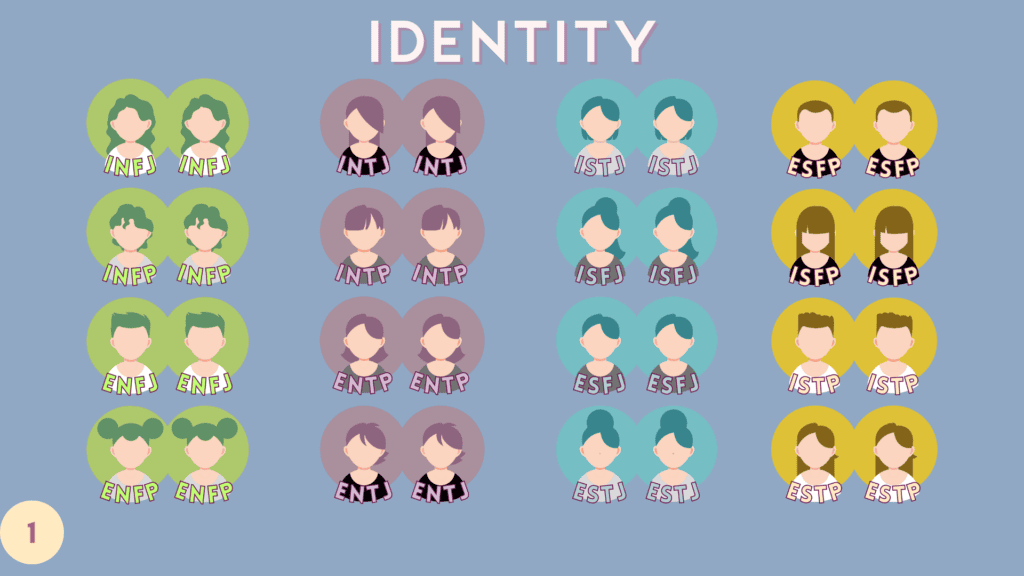
1 – “Identity” Relations
Identity relations are very straightforward, in that, the two partners are of identical type.

Here are the 16 identity pairings for the 16 MBTI types.
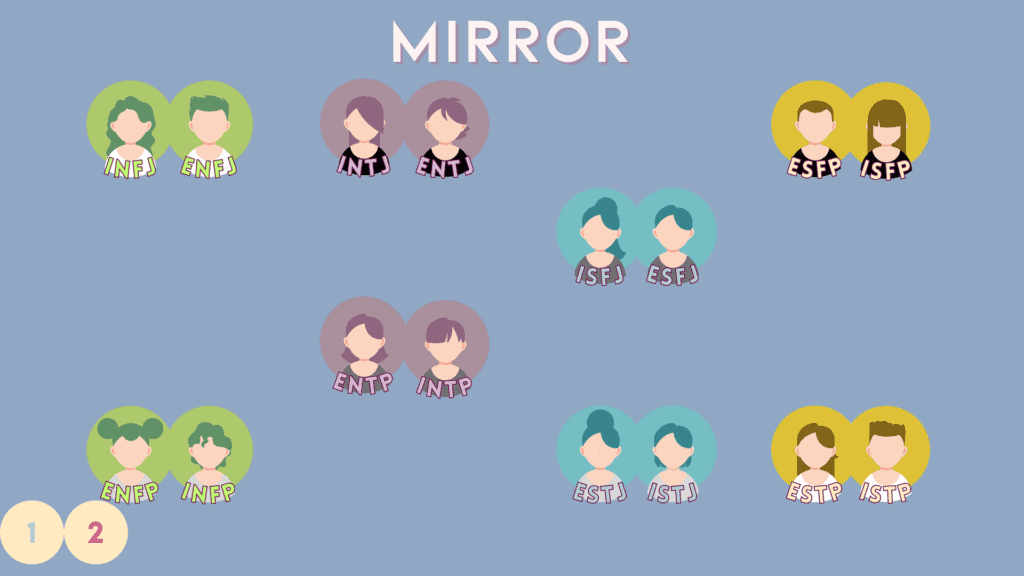
2 – “Mirror” Relations
Mirror types are one another’s introverted or extroverted counterparts. Mirrors are often into similar things or goals in life but at a different degree.

Here are the 8 mirror pairs for the 16 MBTI types.
3 – “Activation” Relations
An activity partner is one that is within the same quadra and of the same attitude, that is both introverts or both extroverts.

Here are the 8 activation pairings for the 16 MBTI types.
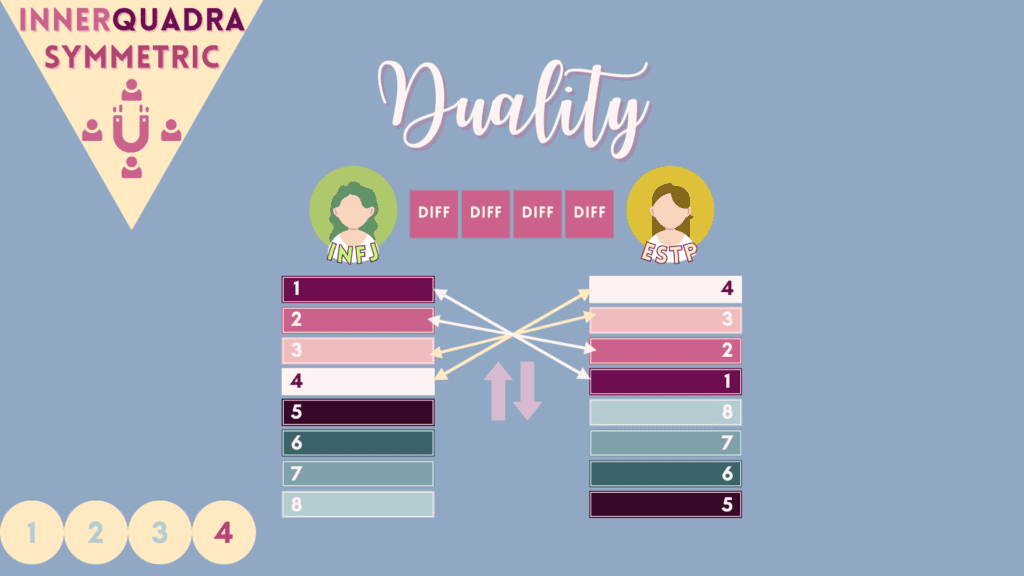
4 – “Duality” or “Dual” Relations
Dual partners share zero letters in common in MBTI type code, which means they are opposite in preferences for all 4 dichotomies of introversion/extraversion, intuition/sensing, feeling/thinking, and judging/perception orientations. However, these partners share all 4 conscious ego functions in reverse order of one another. Duality pairs often have a notably natural attraction to each other.
Here are the 8 dual pairs for the 16 MBTI types.
Outer-Quadra Symmetric Relationships
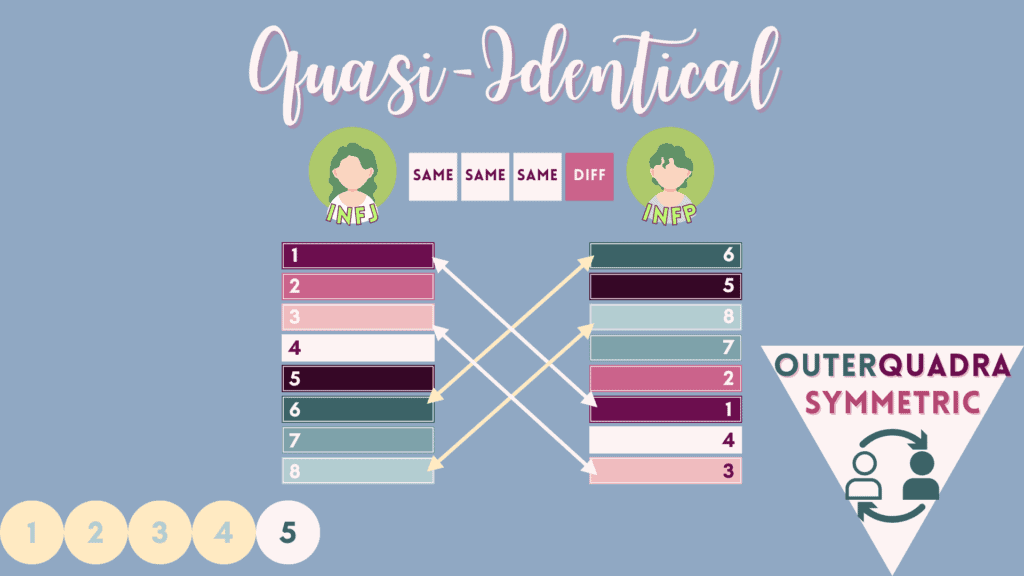
5 – “Quasi-Identical” Relations
Quasi-identical types share the first 3 letters in common and differ in how they orient their judgment or perception. Often there is a lot of mutual respect for each other and an easy-going friendship potential.
Here are the 8 quasi-identity pairs for the 16 MBTI types.

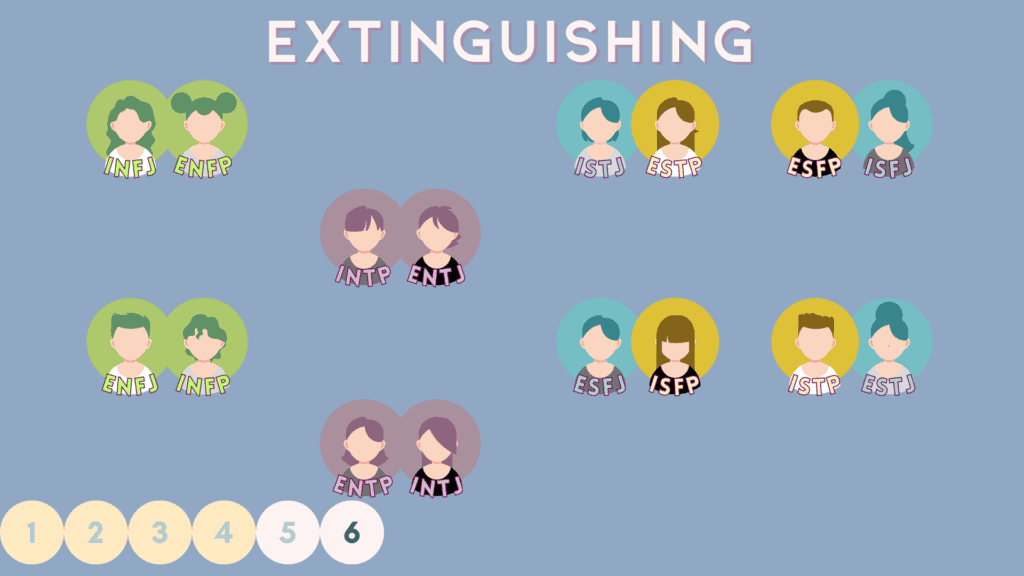
6 – “Extinguishing” Relations
Extinguishing pairs reflect the opposite attitude of each conscious function of one another, which makes partners perfect shadow reflections.

Here are the 8 extinguishing relationships for the 16 MBTI types.
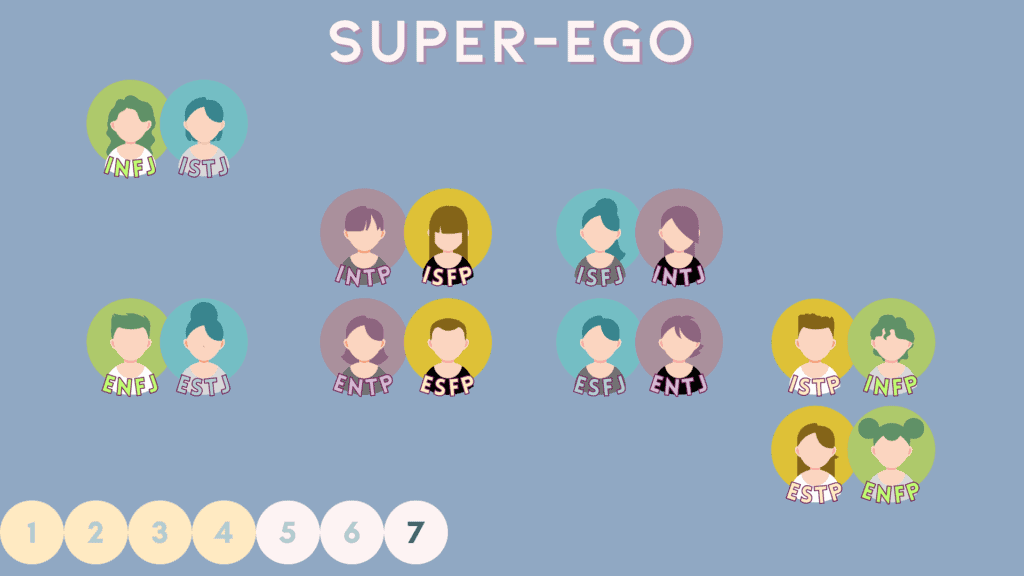
7 – “Super-ego” Relations
Super-ego types are very different types from one another as they are in perfect reverse order of each partner’s functional stack. Although different, there is often a lot of respect for each other’s differences.

Here are the 8 super-ego pairings for the 16 MBTI types.
8 – “Conflict” Relations
Conflict types are characterized by each other’s dominant function being the other’s blindspot function. As a result, difficulties in communication or interaction may arise from extended time together. Due to differences in interests, contrasting preferences to perceive information, and contrasting preferences to make judgments, these types might experience a sense of inability to clearly understand each other and to accomplish their own desires of experience. However, in short periods of interaction, it is usually without issue and can actually be quite a learning experience for each type.
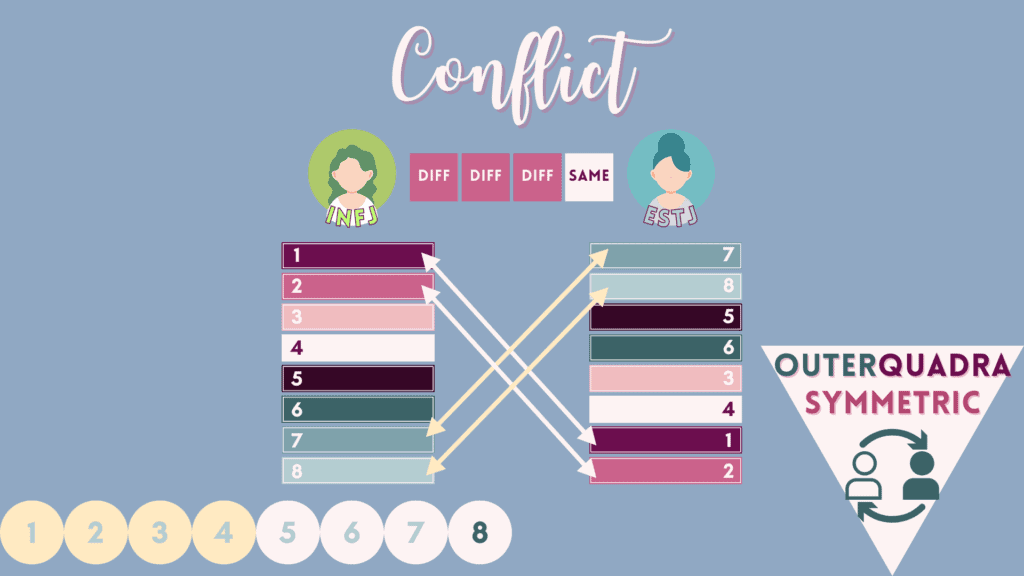
Here are the 8 conflict pairings to keep an eye open for the 16 MBTI types.

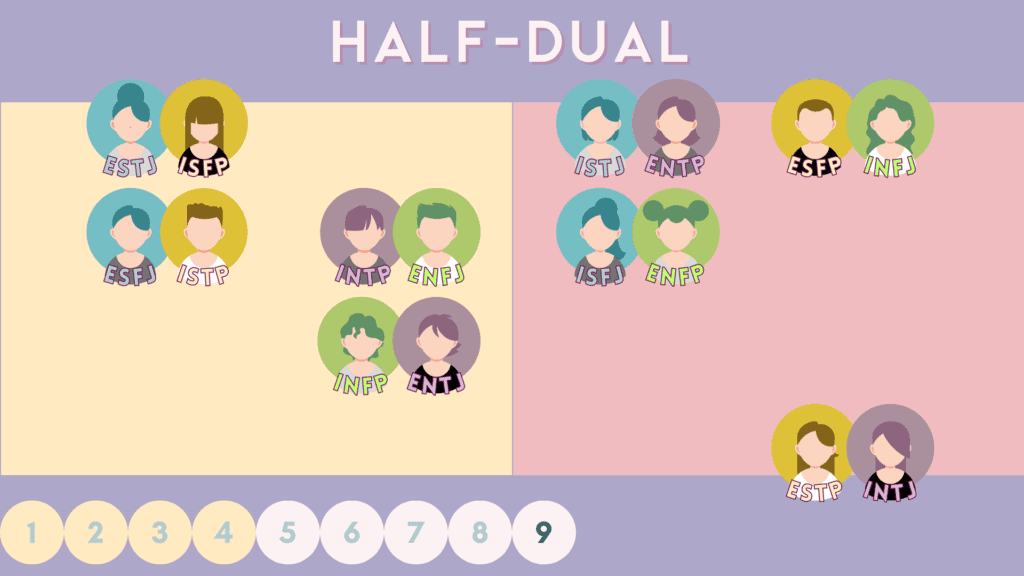
9 – “Half-Dual” or “Semi-Duality” Relations
Semi-duality partners are similar to duality pairings in that each type leads with the other’s inferior, so there is that natural attraction in dualness. However, the auxiliary and tertiary functions differ.

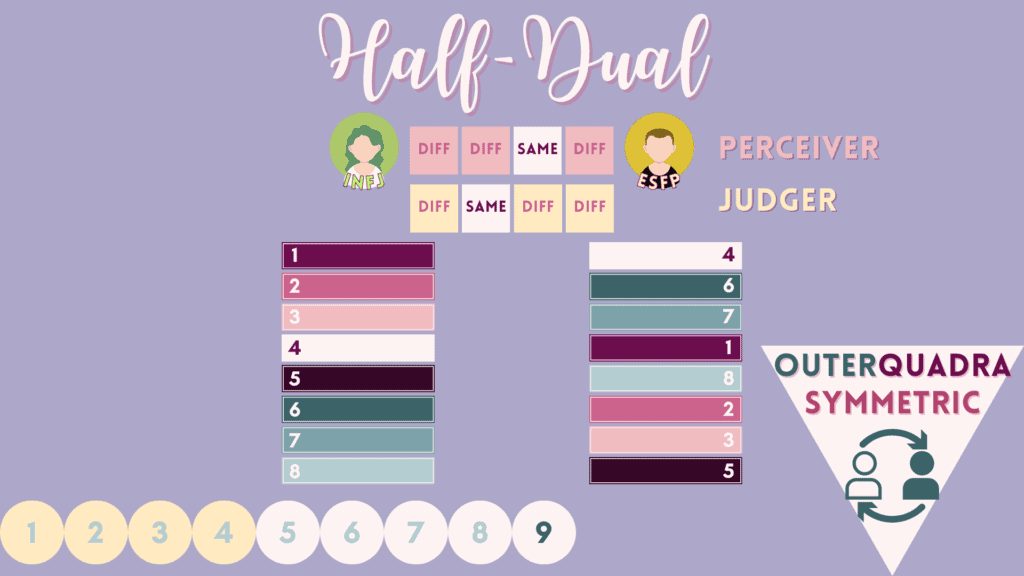
Here are the 8 semi-dual pairings for the 16 MBTI types, categorized by judgers on the left and perceivers on the right.
10 – “Kindred” Relations
Kindred pairs are made of types that share the same dominant and inferior functions. Kindred partners may feel similar at their core, yet have different interests and a difference in how they interact with others.

Here are the 8 kindred pairings for the 16 MBTI types, categorized by judgers on the left and perceivers on the right.

11 – “Mirage” Relations
Mirage are kind of like half-extinguishing partners, in that each partner shares their dominant functions in opposite attitudes. However, their auxiliary and tertiary functions are shared in opposite orders.
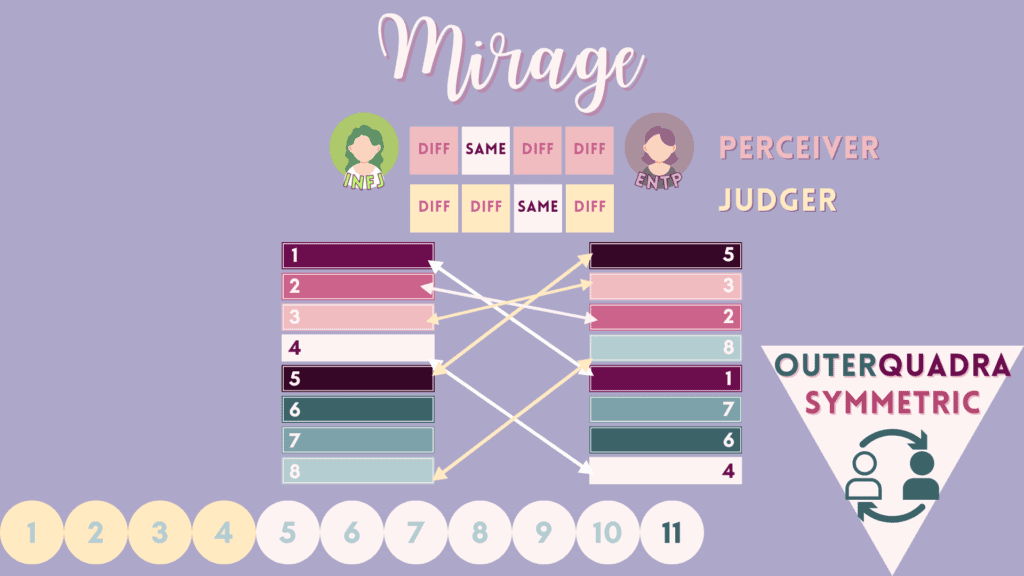
Here are the 8 mirage pairs for the 16 MBTI types, categorized by judgers on the left and perceivers on the right.

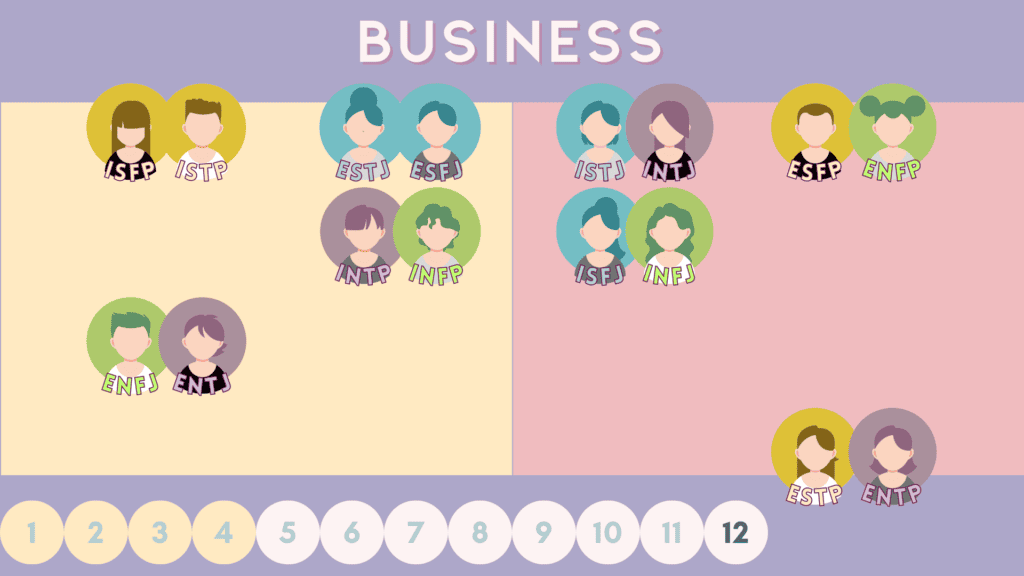
12 – “Business” or “Look-a-like” Relations
Business/lookalike partners are two Socionic types that have mutual auxiliary and tertiary functions. In some ways, they give off a similar vibe yet there will be very obvious contrasts in personality. The name business is used to signify that they can do well in pragmatic matters together, but perhaps not in extended time periods together.
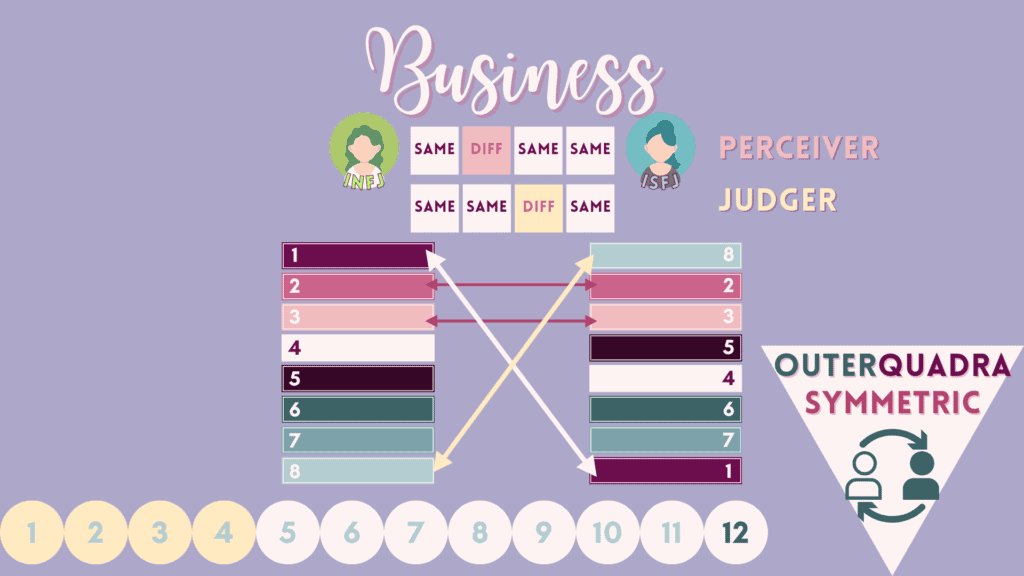
Here are the 8 business pairs for the 16 MBTI types, categorized by judgers on the left and perceivers on the right.
Outer-Quadra Assymmetric Relationships
These relationships are very growth-oriented as they provide ample opportunity to develop weaker cognitive functions through their interactions of this relationship.
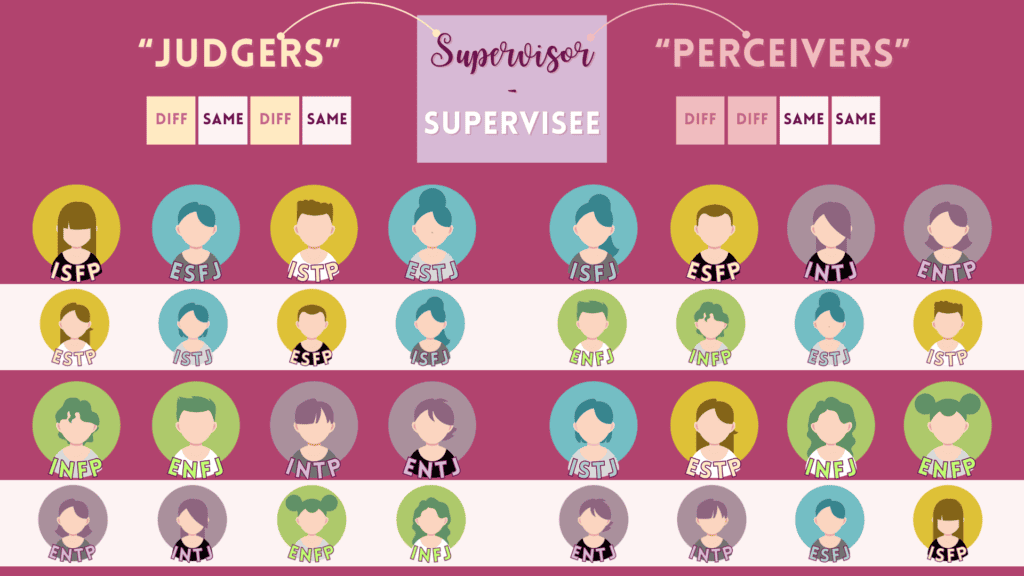
13 & 14 – Supervision or Direct Revision Relations
The supervisor leads with their supervisee’s blindspot, and the supervisee leads with auxiliary function of their supervisor. Each person will sense from the other that they can learn something meaningful from each other in this relationship, sharpening weaker parts of their own personality that they wish to develop more fully.

Here are the 16 supervision/revision relationships for the 16 MBTI types.
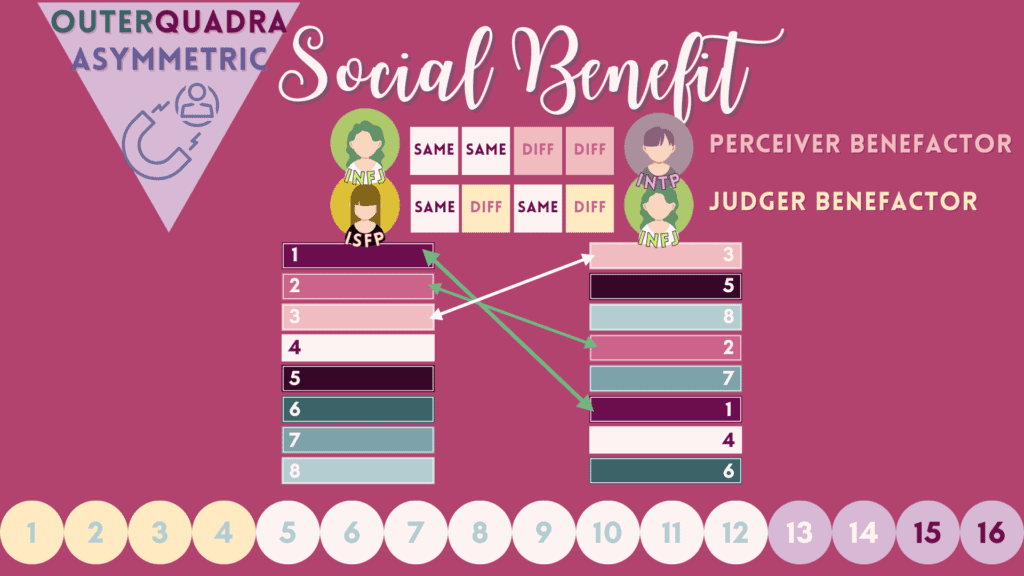
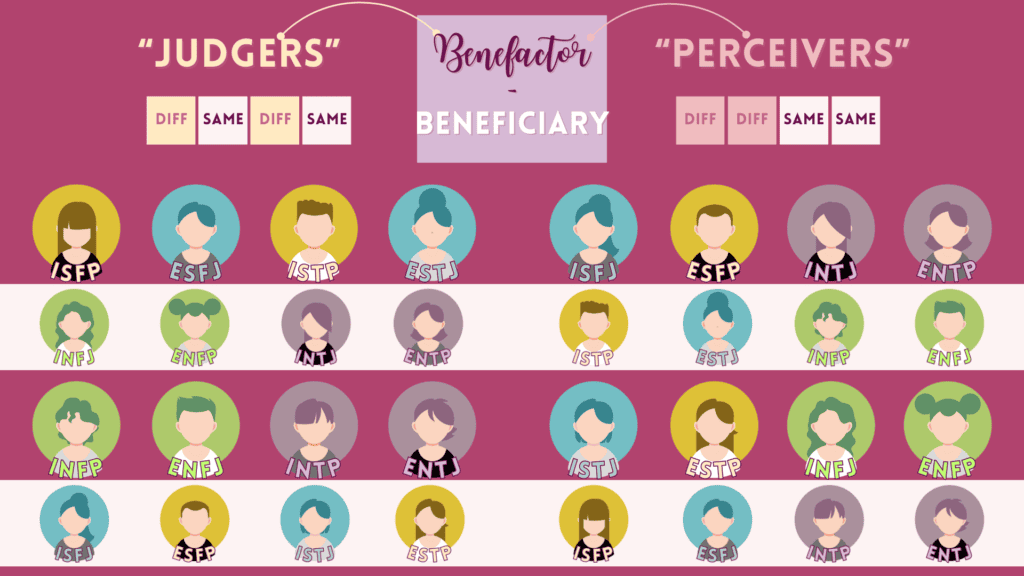
15 & 16 – Social Benefit or Direct Social Request Relations
The social benefactor leads with their beneficiary’s critical parent function. Additionally, the auxiliary of the benefactor is the anima/animus (aspiration) of the beneficiary. In reciprocation, the beneficiary leads with the benefactor’s tertiary function. The partners match one another in introversion or extraversion.
Here are the 16 social benefit/request relationships for the 16 MBTI types.
Conclusion of Intertype Relationships
Intertype relations are such a fun extension to understanding type compatibility in MBTI. It is such a gift that Socionics offers. The theories that have been developed actually go into great detail about what you can expect in each relationship through noticeable patterns. Please visit the individual articles on each intertype relation for examples and further information!
More MBTI Compatibility Between Types
If you liked this article, you might like these compatibility charts offer a description for the relationship with each of the different types on a subjective level.