Growth Mindmap of INFJ Advocate Personality Type
The INFJ Advocate Personality Type
The INFJ personality type is known to be the rarest of the 16 types, estimated at around ~1% of the population. INFJs are distinct in their warmth and unique wisdom. They usually come across as friendly individuals who could easily get along with most people.

One giveaway of this personality type is their natural desire in conversation to listen intently to attempt to understand other people at a deeper level. They attempt to contribute meaningful insight to others. With their idealist temperament, INFJs love to focus on the improvement of individuals, including themselves.
Outwardly INFJs show their emotional warmth, but internally their minds are always thinking on overtime. Their lead cognitive function of introverted intuition (Ni) has a very subconscious nature, which can be mentally taxing to the INFJ. They are deep thinkers with an appreciation for rationality. INFJs are experts at pattern recognition, which they can easily use to apply to people.
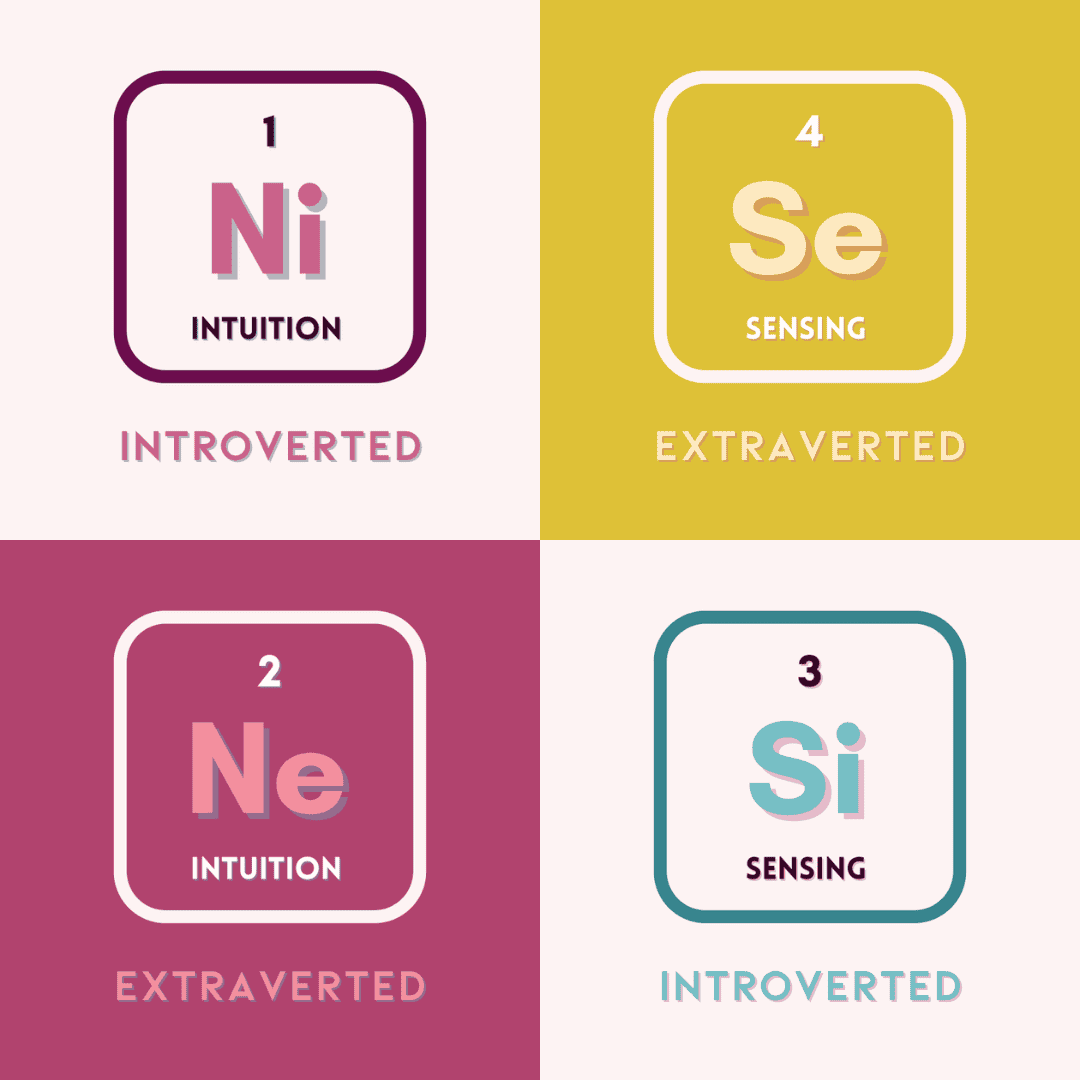
Check out this post for a full breakdown of the INFJ cognitive functions.
You could describe an INFJ as a natural psychologist and they can come across as someone with a sort of counselor vibe to them. People feel at ease opening up to them and INFJs usually welcome vulnerability.
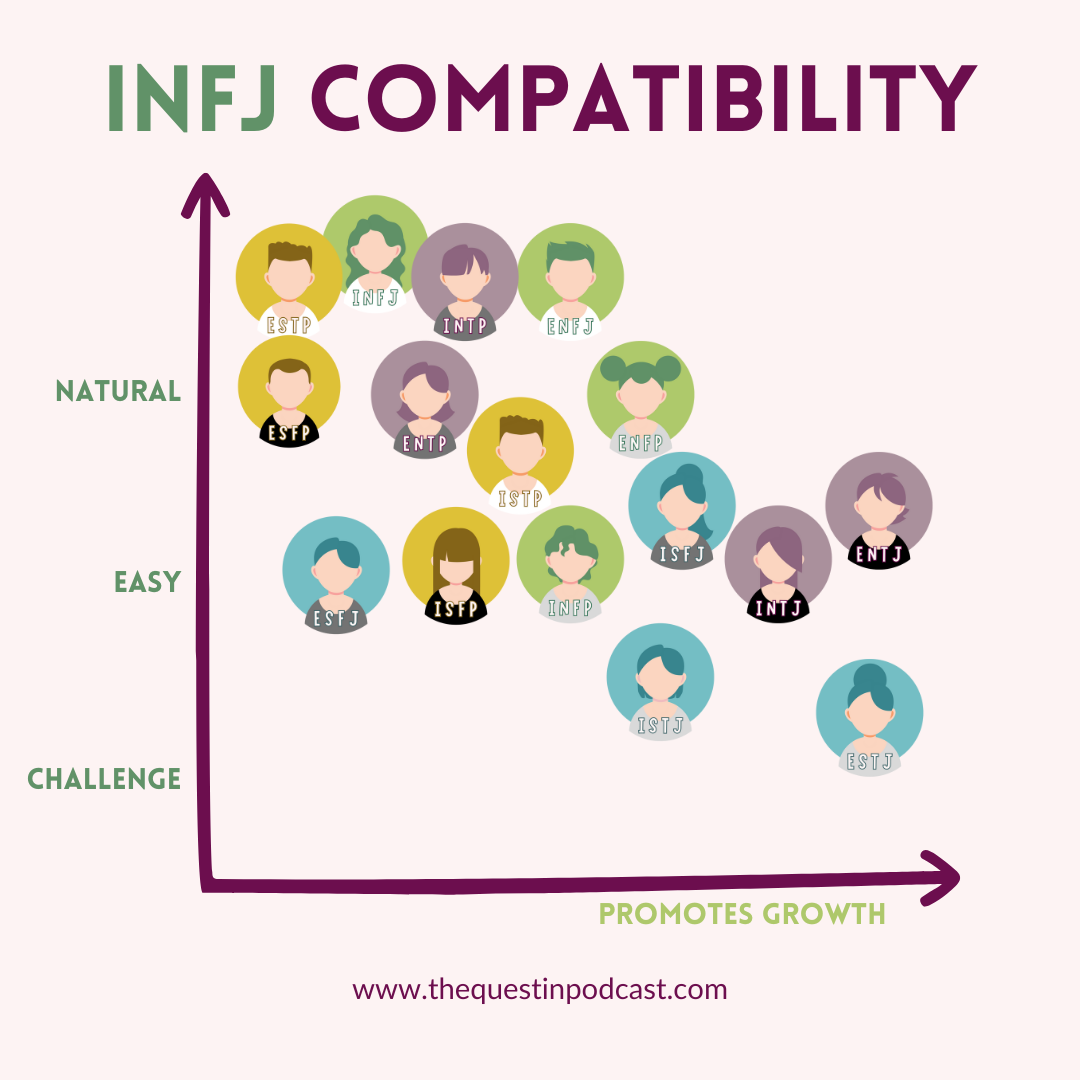
Read this article to learn more about INFJ compatibility with the each of the 16 types.
Introversion vs Extroversion (I vs E) in the INFJ
Some people may misinterpret INFJs as extraverts and may even be mistyped as ENFJ. However, INFJs are true introverts at their core. Because of all the overthinking that could subconsciously go on in the mind of an INFJ, alone time to recharge is mandatory to regularly clear out the mental clutter.
When they have adequate solo thinking time, INFJs can pleasantly interact with others. With this in mind, INFJs appreciate others who respect their personal boundaries and need for quiet time alone.

At the heart of an INFJ is the powerful desire to serve others at a personal level. Because their whole life has been a continual dedication to truly developing themselves, they want to and will readily share resources with others to facilitate growth. They are inclined to help and do well through extroverted interactions.
Though introverted in nature, the INFJ flourishes in community with others and needs to maintain healthy social relationships. Staying in their heads can be a natural comfort, but they have a lot to offer when they bring their ideas to life in the real world.
Intuition vs Sensing (N vs S) in the INFJ
The overactive mind of an INFJ has a natural inclination for intuition versus sensing. In other words, INFJs more easily think and talk about ideas versus events and details. They experience things more readily in their minds than they do in their physical senses.

INFJs are observers, taking in information to process and constantly hypothesizing explanations to reason why things are the way they are.
Intuition is the skill of recognizing what is not physically seen. INFJs like to understand the past and present as points of reference to envision what is inevitable in the future.
Their minds are processing machines that simulate potential possibilities to decide which scenario will be the most likely.
Most times, INFJs live in their minds more than they do in their bodies. Occasionally clumsy in nature, they may not be the most coordinated.
With all the overthinking, the INFJ is uplifted by people who ground them in the present moment through vivid experiences and authentic connections. Though they thoroughly appreciate mentally stimulating thoughts, truly experiencing the world is this type’s highest path of growth.
They must practice somatically experiencing their body, through mindfulness, breathing techniques, and intentional mind-body connection exercises.

Feeling vs Thinking (F vs T) in the INFJ
INFJs are comparably thinkers as much as they are feelers. They love engaging in conversations and have a generous openness to learning about new topics. INFJs appreciate others who desire to teach them and will support the flow of a mentally-stimulating conversation.
A deep talk is a true delight for this type. The analytical ability is a fun skill this type naturally has developed, and it may surprise most people when an INFJ explains their reasonings.
Although INFJs may not be very practical in the systems of the real world, they have a knack for knowledge and can explain things to others in an easily understandable way.
Regarding emotions, INFJs are adept at understanding others but could fail at understanding their own feelings. This is until they intentionally explore their own true values. INFJs desire social harmony with others and putting other people first is a natural inclination of INFJs.
However, they eventually must learn to prioritize fixing their own problems rather than attempting to focus their efforts away. It can take a bit of personal development for an INFJ to mature enough to truly understand their own values and emotions.
Judging vs Perceiving (J vs P) in the INFJ
Though INFJs have a “J” according to the common MBTI 16 personality type preferences abbreviations, they actually are a Perceiver because they lead with introverted intuition (Ni), which is a perceiving function. Perceivers are constantly absorbing information.
INFJs collect data through their experiences in the world and eventually, the things they observe are distilled into principles in their head. INFJs like to seek out the underlying truth behind the scenes of what is seen.
Check out a full post on INFJ Cognitive Functions
Articles you’ll also like if you liked this one…
The INFJ Cognitive Function Stack
-
- Hero Introverted Intuition (Ni) Cognitive Function
- Parent Extroverted Feeling (Fe) Cognitive Function
- Child Introverted Thinking (Ti) Cognitive Function
- Extroverted Sensing (Se) Cognitive Function
- Nemesis Extroverted Intuition (Ne) Cognitive Function
- Critic Introverted Feeling (Fi) Cognitive Function
- Trickster Extroverted Thinking (Te) Cognitive Function
- Introverted Sensing (Si) Cognitive Function